Transformer models can be categorized into three types: Encoder-only, Decoder-only, and Encoder-Decoder models. These models differ primarily in their pre-training approaches.
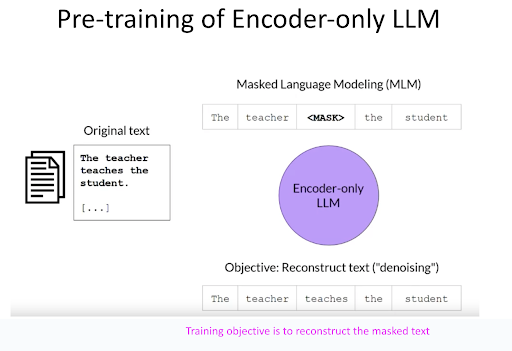
Encoder-only Large Language Models (LLMs) are specifically pre-trained to reconstruct masked tokens. Through extensive pre-training on a vast text corpus, they excel in accurately predicting these masked tokens. As a result, they are particularly effective for tasks like word classification, sentiment analysis, and named-entity recognition.
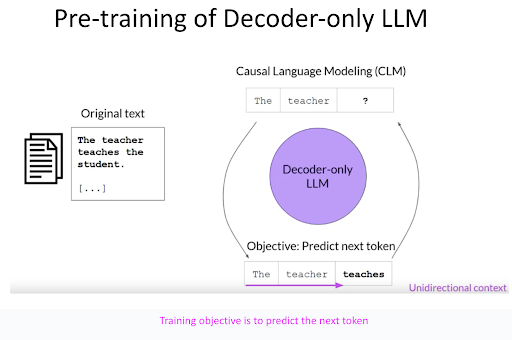
Decoder-only LLMs, on the other hand, are pre-trained with a focus on predicting the subsequent token in a sequence of text. After successful pre-training on a large body of text, they become adept at generating the next token, considering the entire text sequence that has been predicted so far. These models are the backbone for applications such as translation, summarization, and question-answering, with a fundamental strength in text generation. The more advanced models within this category also demonstrate impressive zero-shot inferencing abilities.
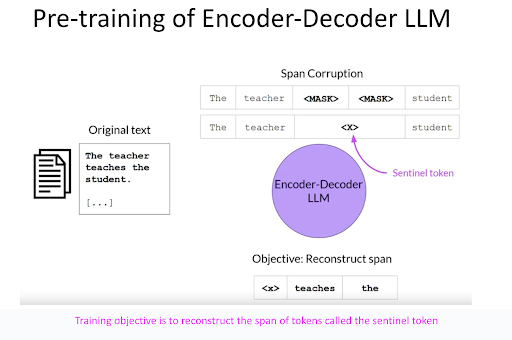
Finally, Encoder-Decoder LLMs undergo pre-training to predict a specific span of tokens, known as sentinel tokens, within a text sequence. The span of these tokens varies during training. After comprehensive pre-training on extensive text collections, these models become proficient at predicting subsequent tokens, taking into account the entire sequence of text already predicted. This makes them highly suitable for tasks like translation, summarization, and question-answering, similar to the decoder-only models.
Now at this point you may be wondering how a decoder-only model like GPT4 is able to excel at tasks such as sentiment analysis and language translation, tasks that decoder-only models are not supposed to excel at. The reason is that decoder-only models like GPT4 have had comprehensive training on vast, diverse text data. This training endows them with a deep understanding of linguistic patterns, contexts, and nuances. Although primarily designed for text generation, their ability to grasp context and detect language patterns enables effective performance in a range of NLP tasks. These models are skilled in pattern recognition, crucial for tasks like translation, and can infer sentiment from textual context, aiding in sentiment analysis. Additionally, their architecture supports versatility, allowing them to adapt to various tasks, often with minimal specific training. GPT4 and similar models leverage extensive pre-training, contextual understanding, and sophisticated design to perform tasks beyond their core generation capabilities, demonstrating their flexibility and advanced NLP proficiency.
Images Courtesy: Deeplearning.ai, Coursera and AWS
See Also: Transformers, Transformer Models